
In the realm of biotechnology, the market for dna fragment synthesis has witnessed an astonishing growth rate, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 15% over the next five years. This rapid expansion is driven by increasing applications across various sectors including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and synthetic biology.
The Unique Characteristics of DNA Fragment Synthesis in Europe
As I delve into the landscape of DNA fragment synthesis within Europe, it becomes evident that several distinctive features characterize this region’s approach to synthetic biology (Synbio). Firstly, Europe’s regulatory framework is notably stringent compared to other global markets. The European Union’s emphasis on safety and ethical considerations ensures that all synthesized fragments adhere to rigorous standards before they can be utilized commercially. This commitment not only fosters public trust but also encourages innovation through responsible research practices.
Find more about custom dna cloning.Furthermore, Europe boasts a rich tapestry of academic institutions and research organizations dedicated to advancing Synbio technologies. Collaborations between universities and industry players are commonplace; these partnerships facilitate knowledge transfer and accelerate advancements in DNA synthesis methodologies. Notably, countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom have emerged as leaders in this field due to their robust funding mechanisms for biotech startups.Moreover, there exists a growing trend towards sustainability within European Synbio initiatives. Many companies are now focusing on eco-friendly approaches to DNA synthesis that minimize waste production while maximizing efficiency—an endeavor aligned with broader EU goals concerning environmental conservation.Lastly, I must highlight the cultural diversity present across Europe which influences consumer preferences and market dynamics related to genetic engineering products. Different nations exhibit varying levels of acceptance regarding genetically modified organisms (GMOs), thereby shaping how businesses strategize their offerings in terms of marketing and product development.
Conclusion
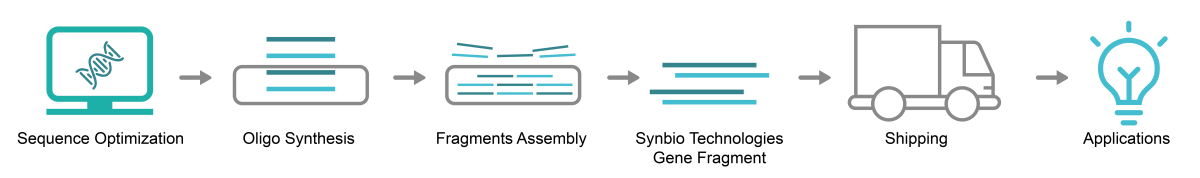
In conclusion, my exploration into the characteristics of DNA fragment synthesis within Europe reveals a complex interplay between regulation, innovation collaboration, sustainability efforts, and cultural nuances. As we move forward into an era where synthetic biology plays an increasingly pivotal role in addressing global challenges—from healthcare solutions to sustainable agricultural practices—the unique attributes inherent within Europe’s market will undoubtedly shape its trajectory on both regional and international stages.

